What is Sustainability?
Executive Factsheet
Meeting “the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” captures the essence of “sustainability” - the natural constraints that present and future generations are facing.
Upload the PDF: What is Sustainability?
What is sustainability? (1)
The term sustainability was coined by the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED) in 1987. WCED’s famous Brundtland Commission Report defines sustainable development as a “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” (WCED, 1987, p. 34). This definition underlines the importance of balancing environmental, societal and economic considerations to improve the quality of life for all.
The challenges (2)
In addition to unprecedented wealth and prosperity, the industrial development of the past two centuries has brought immense environmental challenges, such as global warming, deforestation, and decreasing biodiversity.
- Since 1970, wildlife populations of birds, mammals, reptiles, fish, and amphibians have, on average, declined by over 60%.
- 20% of the Amazon has disappeared in the past 50 years.
- Since the 1980s, the earth has lost about 50% of shallow water corals.
In view of a fast-growing world population (estimated to be 9.8 billion in 2050), the ongoing degradation of our natural systems not only threatens the ecological sustainability of current organizational practices but also the future of our economic and social development.
Excessive human consumption and industrial production have created immense environmental imbalances urging communities of civil society, activists, governments, academics, and practitioners around the globe to advocate for sustainability.
Corporate sustainability and corporate responsibility - It’s the same but different (3)
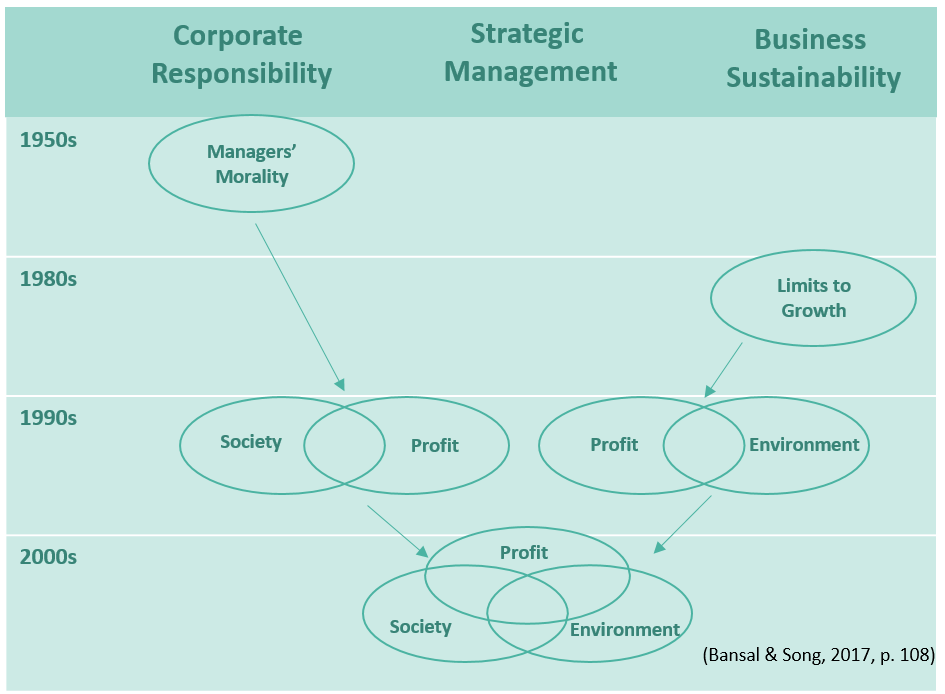
Even though both concepts address the relationship between business and society, corporate sustainability and corporate responsibility have distinct historic origins (Figure 1).
The corporate responsibility debate emerged in the 1950s and mainly focused on the moral responsibilities of managers, taking a normative approach to criticize the amorality of businesses.
The First discussions on corporate sustainability appeared in the 1980s emphasizing on the limits to growth of modern economies. The aim was to apply a system approach to investigate the failures of businesses to preserve natural systems.
Despite having different underlying assumptions, the two debates converged over time, often using the same terms synonymously. Today, scholars disapprove of this handling and press for a better distinction between the two constructs in order to tackle social and environmental challenges more efficiently.
How about businesses? (3)
The successful implementation of sustainability initiatives depends on a range of factors, e.g., the involvement of the firm’s top management team, supportive governance structures as well as a firm’s ability to collaborate with key stakeholder groups such as governments and non-governmental organizations. A strategic focus on sustainability may help to enhance a firm’s environmental performance, optimize resource utilization, and facilitate the development of novel firm capabilities. Yet, to address sustainability challenges, some argue that companies would need to implement business models that are inherently sustainable and promote a circular and low carbon economy.
Figure 1: The Evolution of Corporate Responsibility and Sustainability
REFERENCES
1- World Commission on Environment and Development. 1987. Our common future (Brundtland Report), vol. 383, Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
2- WWF, Living Planet Report, 2018.
3- Bansal, P., & Song, H. C. (2017). Similar but not the same: Differentiating corporate sustainability from corporate responsibility. Academy of Management Annals, 11(1), 105-149.