Over the years, plenty of research has been conducted into managing innovation in fields such as new product development. But perhaps because organization is perceived as an obstacle to creation in fields such as music or fashion design, a lack of research exists when it comes to managing creation across the broad range of, intrinsically, creative industries. This gap in the literature led to what became a 12-year research project involving visits and observation at dozens of creative businesses.
The case studies included the movie producer Pixar, the video game producer Ubisoft, the circus company Cirque du Soleil, the architects of Ateliers Jean Nouvel, Hermès perfumes and the restaurateurs Relais Bernard Loiseau. We conducted a qualitative analysis of what we recorded and identified four key stages of the creative process which will be summarized below.
The following four key stages were observed in each of the 10 case studies we conducted. The four stages do not necessarily occur in a linear fashion.
1. Inspiration
The first stage of any creative process is the search for ideas. This may involve immersion into a different world or setting. It tends to benefit from exposure to distant fields and conversations with those who work among them.
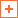
We explored the example of Jean‐Claude Ellena, perfumer for Hermès, who went to India to find inspiration for a new perfume:
“I went to Kerala to find inspiration, and it was there that I decided the perfume that I was going to create. During my first trip, Indians with whom I spoke talked a great deal about the monsoon and its importance for them. I returned two months later to experience the monsoon first hand. It is a season of regeneration, rebirth, blossoming, a moment when the skies and the earth embrace. During the monsoon, nature is still fragile and flowers are barely open. The idea of fragility was interesting for a perfume. The monsoon is also the time when colors and smells are the clearest, the purest. I started working on the idea of dewdrops on flowers. The rebirth associated with the monsoon also evoked the smell of sap, a little unripe and very light. These sensations were quite the opposite of the conventional image of India, full of vibrant colours and hot spices. I was looking for another way to describe India, fresh and natural, a sensation better suited to ‘cold’ spices.”
- Jean‐Claude Ellena, perfumer for Hermès
Photo Credit: ©Shashank / Adobe Stock
The search for ideas may involve immersion into a different world or setting.
This contrasts with the inspiration phase of a French theatre company, “Le Théâtre du Soleil”, that starts with a collective inspiration phase where individuals are enriched by the ideas of one another.
“We call ‘concoctage’ the dedicated time during which the actors discuss, listen, invent together, and exchange ideas without organizing them too much, but just enough to share them on stage.” - Charles‐Henri Bradier, co‐director.
2. Framing
Framing involves moving an idea from the conceptual world to the material world where it can be shared with others. This could be through words, sketches and images, for example. An example of how this can occur is the creation of a new show at Le Cirque du Soleil which used to begin with the founder, Guy Laliberté, launching a theme and some drawings. A small team consisting of the director, the creative director, and Guy Laliberté would then collaborate to come up with the direction that the show will take.
3. Prototyping
Prototyping takes the idea another step closer to the material world. The aim of this stage is to begin to test if the idea is feasible. Prototyping can involve building models or mock-ups, this can take a physical form or it can illustrate structure, in the case of dramatic works it could be a synopsis, for example. At Pixar, we saw how this stage of the creative process involves pitching the idea through story panels, boards and paintings.
“The characters are first drawn in concept until we have a design that we like and believe will work in the film. It is difficult to translate two‐dimensional drawings into three‐dimensional characters. Architects have experience with that, but most character designers do not. We enlist sculptors to reinterpret the drawings into sculpted 3D figures. Both drawings and sculpts are given to the people working on the computer to build and to articulate… For a single film, the story may be hand drawn five full times before this process is complete.”
- Galyn Susman, producer, Pixar.
4. Validation
Validation aims to select, reject or modify the ideas or concepts generated in the previous stages. This tends to involve a decision made by a single individual. Designer Patrick Jouin explained to us the importance, in his view, of selecting ideas:
“Design is also about knowing how to choose the best idea and the right project. Even if one thinks that he has ten good ideas, one idea always stands out from the rest, has more credibility, and brings together all the important qualities such as aesthetics, production, cost, and comfort. This is also the reason why, unlike other agencies, I never present several potential projects to a client and let him choose. I present the client with a single proposition, which may, of course, evolve depending on his comments. Presenting choices and making decisions is my responsibility as a designer.”
- Patrick Jouin, designer.
Even if one thinks that he has ten good ideas, one idea always stands out from the rest, and brings together all the important qualities. - Patrick Jouin
The importance of the individual
Overall we found that in the vast majority of cases, the creative process was handled by a single individual. In these cases, he or she is considered the creator and is in charge of setting the tempo and providing the momentum for the project. Of the four stages we identified, the creator has most responsibility for the validation stage, but nevertheless still often plays a part in the framing and inspiration stages.
Beyond the four stages we identified, the creative process involves iterating and often returning back to one of the four stages, for example framing can often lead to returning to the inspiration stage for help expressing an idea or concept. While every creative process we saw had its own subtle differences, one thing they all shared was in some way, shape or form practicing the four stages we identified.
Learn more on Pixar's model for creativity in this interview with Thomas Paris (in French):
Interview of Professor Thomas Paris on his report on Pixar's model to maintain creativity, on Xerfi Canal (in French).
Learn about the creation management caracteristics (in French):