How AI Is Shaping the Workplace and Workforce Development
Artificial intelligence is transforming the way we work, impacting everything from daily tasks to long-term strategies across industries. While some may see AI as just another technology trend, it’s quickly proving to be much more: a powerful force redefining job roles, enhancing employee capabilities, and reshaping the skills businesses need to succeed. For companies, understanding and integrating AI effectively is becoming not just an advantage, but a necessity.

This article is based on the insights shared during a recent masterclass in Zurich, where leading experts discussed how AI is already transforming workplaces and workforce development. Dr. Peter Fischer, director of HEC Paris’s AI in Marketing Strategy executive program, shared his expertise on the ways AI can boost employee engagement, learning, and operational efficiency. Joining him were Dr. Anne Scherer from DeltaLabs and Dr. Sina Wulfmeyer, Chief Data Officer at Unique, who brought a blend of practical and academic perspectives on applying AI effectively in various business settings. Together, these experts paint a clear picture of AI’s current and future impact on work, debunking myths, addressing ethical concerns, and sharing real-world examples of how companies can make AI a driver of innovation and growth.
Leveraging AI in the workplace
AI is transforming workplace functions in powerful ways, starting with marketing and extending to a range of departments that stand to benefit from smarter automation and data-driven insights.
Key functions where AI is most adopted
Marketing is at the forefront of the AI-driven revolution. According to recent findings from the 2024 Stanford AI Index Report, marketing stands out as the industry that both pioneers and dominates the implementation of AI technologies across various sectors.
Why is marketing so AI-friendly? AI enables marketing teams to automate processes and personalize customer interactions on an unprecedented scale. Contact center automation, for example, is an area where AI excels by efficiently managing high volumes of customer interactions while ensuring consistency in response quality. Through natural language processing, AI-powered chatbots can handle initial queries and basic problem-solving, allowing human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Beyond automation, personalization has become AI’s superpower in marketing. The ability of AI models to sift through vast amounts of customer data allows brands to tailor messages and offerings at a granular level. For instance, AI-driven personalization can identify consumer preferences and purchasing behavior, making it possible to send the right message to the right person at the right time. As Anna Scherer, an AI expert and founder of a generative AI company, puts it, “With large language models, you can now have hyper-personalized communication.”
Coca-Cola, for example, has taken this a step further, creating over 2,200 customer personas to hyper-personalize its communications – an achievement that would be nearly impossible without AI.
Customer acquisition is yet another area where AI proves invaluable. Through predictive analytics and machine learning, companies can assess potential leads and forecast which prospects are most likely to convert, allowing sales teams to prioritize high-value leads. This data-driven approach means that marketing efforts are not just broad strokes but are informed by real-time insights, giving companies a substantial edge in their strategies.
Potential benefits across departments
While marketing may lead to AI adoption, the potential for AI to deliver value spans far beyond. Departments like product development and operations management are beginning to uncover substantial advantages, though adoption here is often more measured. The reason? Unlike marketing, where the immediacy of customer interaction demands innovative tools, these areas require a slower, strategic integration of AI to ensure that its benefits align with organizational goals.
In product development, AI offers transformative possibilities. From predicting trends to optimizing design processes, machine learning models analyze vast datasets, helping teams create products that are better aligned with market needs. AI can also accelerate the R&D timeline by automating simulations and analyzing test results, giving teams the freedom to focus on creative and innovative aspects of product creation.
Operations management, another fertile ground for AI, can leverage data to streamline logistics, supply chains, and quality control. Imagine predictive maintenance for factory equipment: AI algorithms analyze machinery data to forecast maintenance needs, reducing unexpected downtimes and optimizing productivity. In supply chains, AI can help manage inventory by predicting demand fluctuations, ensuring that products are available when needed without overstocking.
However, the journey toward full AI integration is not universal, with some industries remaining cautious. In sectors like pharmaceuticals and human resources, companies face unique regulatory and ethical constraints. For example, in HR, while AI can be used for tasks like screening candidates or managing schedules, there is a clear hesitance to apply it more deeply without assurances that these systems remain unbiased. “People want to experiment but in a safe environment”, notes Anna Scherer. This balancing act between innovation and caution shapes how industries approach AI, especially where sensitive data and high stakes are involved.
As AI technology matures and concerns about data security and compliance are addressed, the departments that stand to gain the most will likely begin to adopt AI at a faster pace. For now, each industry finds its rhythm, weighing the real-world benefits AI can deliver against the caution needed to ensure its safe and ethical use.
AI and employee empowerment – new opportunities for learning and growth
AI is not only transforming work tasks but also how employees feel about their roles and career development.
Impact of AI on employee engagement and meaning at work
In workplaces where AI is well-integrated, employees often experience a newfound sense of purpose and engagement. Dr. Peter Fischer’s recent research illustrates this positive trend, showing that employees in AI-empowered environments feel more connected to their roles and more invested in their work. When AI takes on repetitive or routine tasks, employees are freed to focus on areas that require creativity, problem-solving, and decision-making – elements that often contribute to a greater sense of fulfillment.
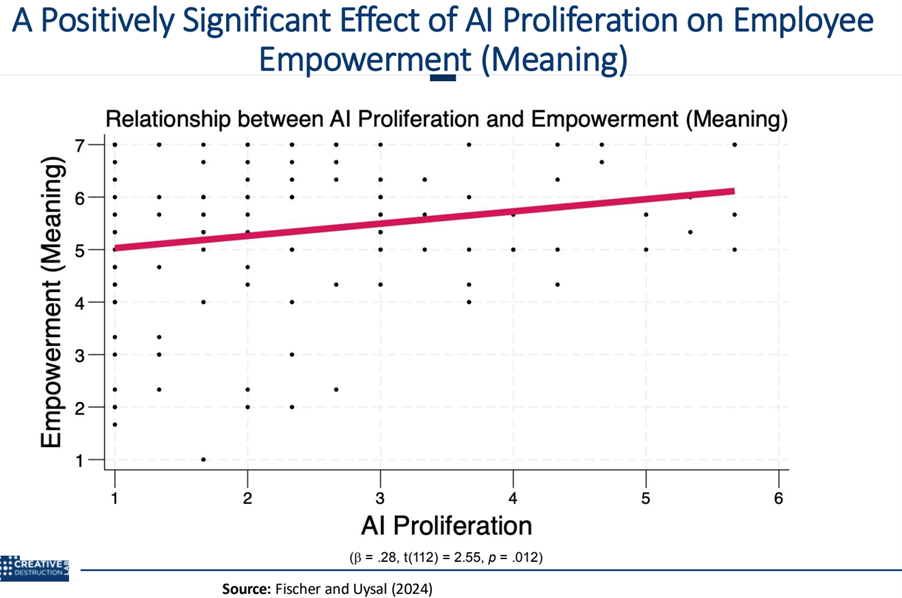
However, Dr. Fischer’s findings reveal a notable distinction: employees with quantitative or technical skills – those comfortable with data analysis or familiar with basic AI concepts – tend to experience this empowerment more acutely. For them, AI is a tool that enhances their expertise, enabling them to operate more effectively and confidently. On the other hand, employees without a strong technical background may feel apprehensive or even marginalized by the rapid infusion of AI in the workplace. This disparity emphasizes a critical need for ongoing education and support, as Peter Fischer points out: “We’re not just training machines; we’re training people to maximize the benefits of AI for themselves.”
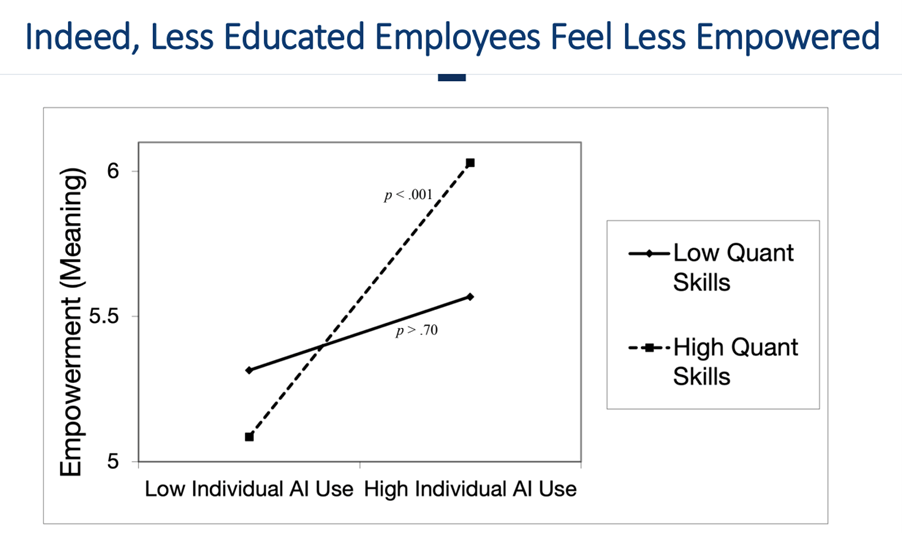
Bridging this gap starts with accessible, company-wide training programs that demystify AI for all employees. Rather than expecting everyone to become an expert, these programs aim to provide a foundational understanding of AI’s capabilities and limitations, fostering a culture where everyone can contribute to and benefit from AI-driven processes. When employees feel equipped to work alongside AI, it becomes less of a disruptive force and more of an empowering resource, opening doors to continuous learning and professional growth across all levels of the organization.
Training with AI – practical examples from HEC Paris
HEC Paris has taken an innovative approach to AI training, using interactive exercises that bring the technology to life for MBA students. One standout example involves Nao, a humanoid robot that serves as both an advisor and a challenging audience. In this two-step exercise, students begin by working with Nao as a supportive mentor, using its insights to craft a pitch that would convince a venture capitalist. Nao provides feedback on everything from structure to delivery, helping students refine their message with an AI-powered perspective.

Once they’ve honed their pitch, students face the ultimate test: Nao switches roles from helpful advisor to critical venture capitalist. Now, the students must deliver their pitch convincingly, navigating the dynamic of presenting to an AI with real-time analysis capabilities. This process not only strengthens their pitching skills but also reinforces the concept of human-machine interaction, as they learn to leverage AI’s feedback in a realistic, high-stakes scenario.
These exercises exemplify how similar methods could be applied in corporate training. By using AI-driven tools as mentors and evaluators, companies can offer employees hands-on experience with the technology, helping them understand its capabilities and limitations. Such training not only builds familiarity but also demonstrates how AI can be a collaborative tool rather than just a replacement. For instance, employees could practice customer service skills with an AI agent or simulate client interactions to refine sales pitches, all while receiving actionable feedback. This type of immersive learning positions AI as a valuable partner in professional growth, equipping employees to better integrate AI into their daily roles.
Addressing challenges and misconceptions around AI
As AI adoption grows, companies must address both practical challenges and temper the hype to unlock its true potential.
Data privacy and ethical concerns
As AI becomes more deeply integrated into business operations, concerns around data privacy and ethics come sharply into focus. High-profile incidents, like the case involving Samsung employees who inadvertently leaked sensitive proprietary code into a public AI tool, underscore the need for robust safeguards. In highly regulated industries such as finance and healthcare, where data security is paramount, organizations are understandably cautious about deploying AI without secure, structured frameworks.
One key solution is the use of “retrieval-augmented generation” (RAG) models. These systems keep sensitive data safely within the company’s internal network while still leveraging AI’s capabilities.
Instead of sending information to external servers, RAG models allow companies to access insights from internal data sources without exposing proprietary or confidential information to third parties. This approach addresses the core fear that using external AI services could lead to unintended data leaks, as was the case for Samsung.
Additionally, establishing secure internal AI environments provides employees with a controlled space to experiment with AI-driven tools. Companies can create clear guidelines around data use, ensuring employees understand which tools are approved and which types of information can be safely used. “People want to experiment but in a safe environment”, explains Sina Wulfmeyer. With these safeguards in place, businesses can encourage innovation without compromising data privacy, setting the stage for responsible and effective AI adoption.
Moving beyond the hype – realistic AI applications and limitations
The excitement surrounding AI has led to its fair share of hype, with some proclaiming that it will soon replace entire job functions. However, the reality within businesses paints a more nuanced picture. While AI can indeed improve efficiency, most applications today are designed to enhance – not replace – human roles. In sectors like banking, for example, AI is being used for automated customer support. AI-powered tools can handle initial queries, direct customers to appropriate resources, and provide quick answers to frequently asked questions. This frees up human agents to focus on more complex, relationship-driven interactions, allowing them to deliver a better customer experience without being stretched thin by repetitive tasks.
AI adoption often starts with simpler applications, where it can provide immediate, visible value. One such example involves an AI module implemented in a Swiss bank’s cafeteria to help employees locate the best dining options for the day.
This may sound trivial, but starting with these low-stakes uses allows companies to familiarize themselves with AI technology in a controlled, low-risk environment.
As companies build trust and confidence in AI, they progressively move to more complex applications. In banking, AI is now being used for tasks like portfolio optimization, where it can analyze vast amounts of data to suggest potential investments tailored to a client’s preferences. This kind of application demonstrates the real value of AI: enhancing decision-making through data-driven insights rather than replacing the human advisor’s judgment.
Adopting AI gradually allows organizations to scale up thoughtfully, ensuring that each new implementation aligns with their goals and integrates seamlessly into existing workflows. This measured approach to AI adoption tempers the hype and shows that, for many companies, the goal isn’t full automation but smarter augmentation.
Preparing for an AI-enhanced future – the role of continuous learning and adaptation
By implementing comprehensive AI training programs and fostering a culture of lifelong learning, businesses can ensure their workforce is not only proficient with AI tools but also confident and forward-thinking, ready to lead in an AI-driven world.
Upskilling and reskilling for AI proficiency
Companies have a choice in how they approach AI training: offering mandatory courses, encouraging voluntary learning, or taking a blended approach with continuous education programs. Each of these methods has its strengths, but the goal remains the same: helping employees become proficient in using AI tools and understanding their practical applications.
One effective strategy is to identify and empower “AI champions” within the organization. These are individuals who are enthusiastic about AI and eager to explore its potential. By training these early adopters in advanced AI skills, companies create a group of internal advocates who can share their knowledge, inspire others, and facilitate a culture of AI curiosity and innovation. This peer-driven approach can be especially effective in fostering widespread acceptance and enthusiasm for AI.
Swiss bank Pictet offers a compelling example of AI training in action. The bank has implemented a structured program that includes both introductory and advanced AI courses, allowing employees to learn at a comfortable pace.
For those who prefer a more flexible approach, Pictet also provides voluntary sessions where employees can dive deeper into AI topics relevant to their roles. By making AI education accessible and varied, the bank supports employees at all skill levels, encouraging them to integrate AI into their daily tasks confidently.
This focus on continuous learning aligns well with the fast-evolving nature of AI technology. Rather than viewing training as a one-time effort, companies like Pictet emphasize the importance of staying up-to-date. As new tools and applications emerge, employees who regularly update their skills are better equipped to leverage AI for creative problem-solving and strategic decision-making.
Building a culture of lifelong learning
To foster a culture of continuous learning and equip teams for the AI era, HEC Paris Executive Education offers customized corporate programs designed to empower your organization. These programs provide a holistic understanding of AI, delving into its potential across various functions, not just marketing.
Through immersive workshops and real-world case studies, your teams will explore essential topics such as data ethics, human-computer interaction, and strategic AI implementation. This hands-on approach ensures participants gain the skills to implement AI responsibly and drive innovation.
Our programs go beyond theory, challenging teams to develop practical AI strategies tailored to your company's specific goals and challenges. We'll work closely with you to design a learning experience that fosters a confident, forward-thinking workforce ready to lead in an AI-driven world.
Contact us to discover how our custom programs can prepare your organization for the AI revolution.